Introduction of AJAX:-
AJAX is a technique for creating faster, and more interactive web applications with the help of XML, HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. It is a web browser technology which is independent of web server software.
AJAX use of the built-in browser XMLHttpRequest (XHR) objects to send and receive information to and from a web server asynchronously, in the background, without blocking the page or interfering with the user's experience.
Ajax uses XHTML for the content, CSS for designing, along with Document Object Model and JavaScript for dynamic content display. Before AJAX technology, the web applications transmit information to and from the server using synchronous requests. It this we fill out a form, hit submit, and get directed to a new page with new information from the server. But with AJAX, when we hit submit, JavaScript will make a request to the server, interpret the results, and update the current screen.
We can guess the popularity of AJAX, such that we hardly find an application that doesn't use Ajax to some extent. The example of Ajax-driven online applications are Gmail, Google Maps, YouTube, Facebook, and so many other applications.
How Does AJAX Work?
JavaScript and XML combine to make asynchronous updating happen through the use of something called an XMLHttpRequest (XHR) object. When the user visits a web page which is designed using AJAX technology, and a prescribed event occurs (a button, or fills out a form) the JavaScript creates an XMLHttpRequest (XHR) object, which then transfers data in an XML format between a web browser and a web. The XMLHttpRequest(XHR) object sends a request for updated page data to the web server, the server process the request, a response is created at server-side and sent back to the browser, which then uses JavaScript to process the response and display it on the screen as updated content.
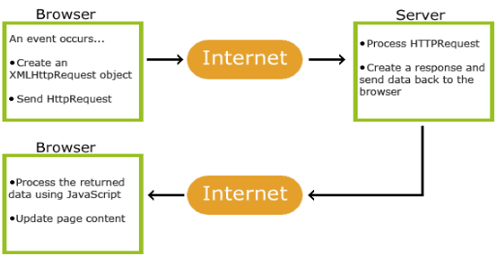
Summary:-
The JavaScript automates the updating process, the request for updated content is formatted in XML to make it understandable, and JavaScript again refreshes the relevant content for the user viewing the page. Whereas the AJAX technique ignores extraneous page data and only handles requests for updated information and the updated information itself. This shows the AJAX's effectiveness, as it makes the websites and applications that use AJAX faster and more responsive to users.



